In the dynamic realm of digital finance, “What is cryptocurrency?” emerges as a fundamental question. Cryptocurrency, also known as crypto, represents a revolutionary form of digital or virtual currency secured by cryptography. Operating without a central authority, it challenges traditional financial norms, fostering inclusivity and resilience. The decentralized system, facilitated by blockchain technology, ensures transparent and secure transactions, making cryptocurrency more than just a digital currency—it signifies a decentralized revolution in the financial landscape.
What Is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a form of digital currency that is created, managed, and exchanged using advanced encryption techniques called cryptography. It emerged along with blockchain technology as a decentralized alternative to traditional fiat currencies and is exchanged between peers without the need for banks or other centralized authorities.
The first and most well-known cryptocurrency is Bitcoin, created in 2009. Since then, countless other cryptocurrencies have emerged – referred to as “altcoins” – as competitors or alternatives to Bitcoin. Some notable ones include Ethereum, Litecoin, and Ripple.
Cryptocurrencies leverage blockchain technology to achieve decentralization, transparency, and immutability. Transactions are verified and recorded in a public blockchain ledger, avoiding manipulation or control by a single authority.
Units of cryptocurrency are created through a process known as mining. This involves using specialized computing hardware to solve complex mathematical puzzles to create new blocks in the blockchain, and miners are rewarded with newly minted cryptocurrency as an incentive.
Due to their digital nature and use of encryption, cryptocurrencies allow for anonymous transactions between parties absent of middlemen. This has made cryptocurrencies popular for securing and verifying financial transactions, though also controversial due to their use for illegal activities.
Overall, cryptocurrency represents a major technological leap in how we exchange and secure value, though widespread mainstream adoption is still limited by factors like price volatility and regulatory uncertainty. As the space continues to mature, cryptocurrencies could ultimately displace traditional forms of money one day.
| Next Up In Investing |
| Cryptocurrency: Step by Step Guide for Beginners |
| How Many Cryptocurrencies Are There? |
| How Does Cryptocurrency Work? Blockchain Tech |
| Is Cryptocurrency a Scam? |
Understand Cryptocurrency?
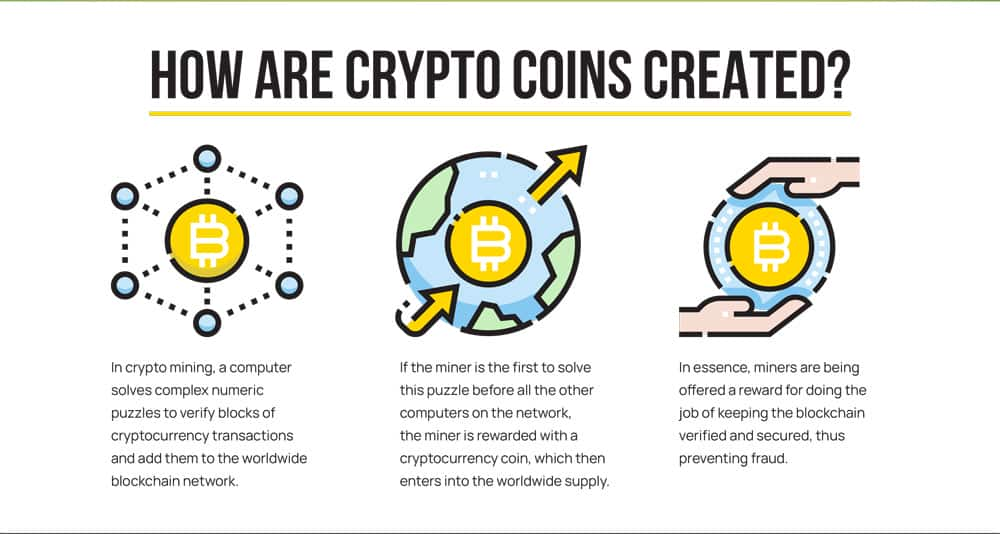
To fully understand cryptocurrencies, it helps to dive deeper into some of their key distinguishing features:
- Decentralized – No central authority controls cryptocurrency networks. They are maintained collectively by an open, distributed network of computers. This makes cryptocurrencies censorship-resistant and resilient.
- Secure – Cryptocurrencies rely on cryptography for things like generating currency, verifying transactions, and securely storing funds. Advanced encryption provides strong protections against fraud or data tampering.
- Transparent – Every cryptocurrency transaction is recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain that can be accessed and verified by anyone. This provides transparency while still allowing anonymity.
- Scarce – Many cryptocurrencies have a limited total supply of tokens that will ever exist. Along with demand, this scarcity establishes their value and can drive up prices.
- Programmable – The programmable nature of cryptocurrency protocols enable developers to build sophisticated functionality, applications, and features on top of them.
- Fast and global – Cryptocurrency transactions are processed rapidly, are irreversible, and can be sent anywhere in the world with an internet connection.
By utilizing cryptography, blockchain technology, and decentralized networks, cryptocurrencies offer significant advantages in security, privacy, transparency, and efficiency compared to traditional currencies and financial systems. Their innovative approach enables a fundamentally new type of digital asset.
Who invented cryptocurrency?
The identity of the person or group who created Bitcoin is still unknown. Bitcoin was first outlined in a whitepaper released under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008. The whitepaper laid out technical details for a “peer-to-peer electronic cash system” based on cryptography and a blockchain network.
In early 2009, Nakamoto released the first version of the Bitcoin software and mined the genesis block, marking the official start of Bitcoin. Throughout 2009 and 2010, Nakamoto collaborated with various early Bitcoin developers to further develop the software and network.
In mid-2010, Nakamoto handed over control of the source code repository and network alert key to Gavin Andresen, a lead developer, and faded from public view. Nakamoto’s real identity remains unknown; theories point to candidates like computer scientists Nick Szabo or Hal Finney.
Other major cryptocurrencies were created by known individuals or teams:
- Ethereum – Proposed in 2013 by Vitalik Buterin and launched in 2015. Buterin leads the ongoing development.
- Litecoin – Created in 2011 by Charlie Lee, a former Google engineer. Lee aimed to build on Bitcoin’s technology with some key tweaks.
- Ripple – The Ripple payment network was created by Chris Larsen and Jed McCaleb and launched in 2012. The XRP cryptocurrency is an integral part of their network.
- Monero – Launched in 2014 by a collective going by the pseudonym Nicolas van Saberhagen. The goal was to create a secure, private cryptocurrency.
So while Bitcoin’s creator remains anonymous, the origins of all other major cryptocurrencies today are known. The identity of Satoshi Nakamoto continues to be one of the great mysteries in the history of cryptocurrency.
Cryptocurrency vs. traditional currency
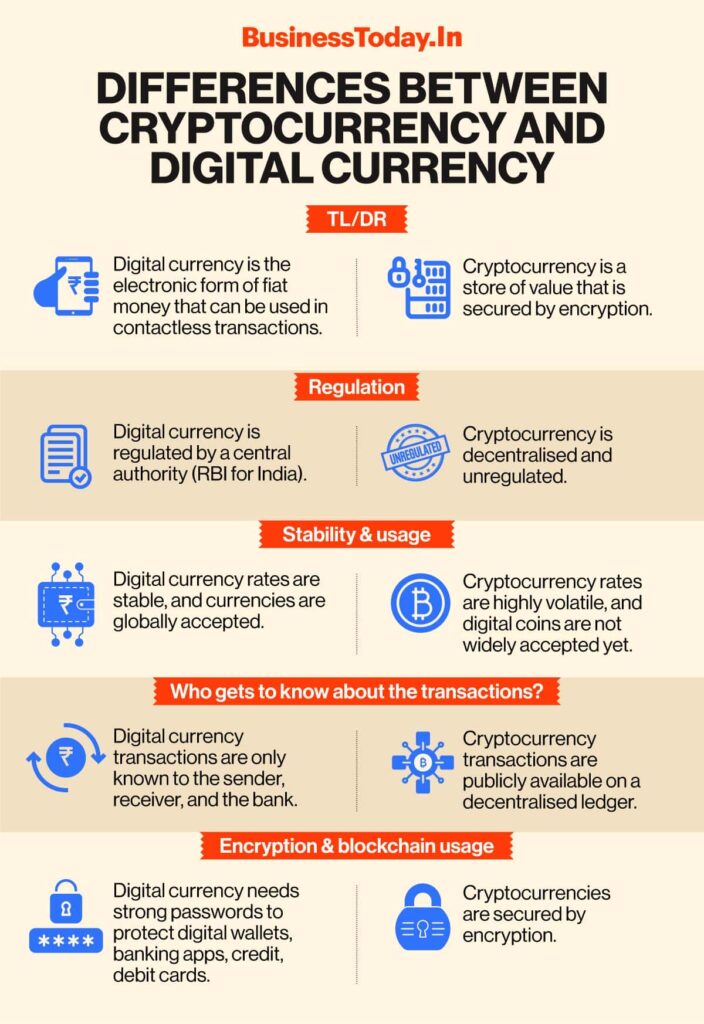
There are several key differences between cryptocurrency and traditional fiat currency like U.S. dollars or euros:
- Cryptocurrency is decentralized and managed by peer-to-peer networks whereas traditional currencies have central authorities like central banks and governments.
- Cryptocurrencies are purely digital assets whereas traditional currencies have physical representations like coins and paper bills.
- Transactions in cryptocurrency are recorded on public blockchains while traditional banking transactions are private.
- Cryptocurrencies rely on advanced cryptography for things like security and generating currency. Traditional currencies do not utilize encryption techniques.
- The supply of many cryptocurrencies is preprogrammed and capped while national currencies have flexible and inflationary supply.
- Cryptocurrency transactions are irreversible while credit card or bank payments can be reversed or disputed.
- Cryptocurrencies can be traded 24/7 globally whereas forex markets have defined open and close times.
- Cryptocurrency values can be highly volatile compared to relatively stable national currencies.
In summary, cryptocurrencies operate very differently from traditional currencies that are issued by central banks. They utilize groundbreaking technology like blockchains and cryptography to facilitate digital transactions without centralized control or oversight. This leads to significant differences in aspects like security, supply, and transmission.
Types of Cryptocurrency
While Bitcoin is considered the original and most established cryptocurrency, there are now over 9,000 other cryptos in circulation. Here are some major types and examples:
- Bitcoin Alternatives – Cryptocurrencies designed to improve on Bitcoin’s limitations or technologically outdated aspects – Litecoin, Bitcoin Cash, Monero
- Stablecoins – Cryptocurrencies pegged to another asset to minimize volatility – Tether, USD Coin, Dai
- Utility tokens – Tokens tied to a product or service on a blockchain platform rather than a cryptocurrency itself – Basic Attention Token, Binance Coin, Chainlink
- Meme coins – Cryptocurrencies based on viral internet memes and jokes – Dogecoin, Shiba Inu
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) – Digital forms of fiat money issued by central banks – the digital yuan, e-krona
- Security tokens – Cryptocurrencies that represent an investment in an underlying asset like real estate or equity – Augur, Polymath
- Exchange tokens – Native tokens generated by a cryptocurrency exchange – Binance Coin, FTX Token, Crypto.com Coin
- Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) – Unique cryptographic tokens that represent ownership of a digital asset like art – Bored Ape Yacht Club, CryptoPunks
This is just a small sample of the wide range of cryptocurrency types innovated since Bitcoin. While their functions and features vary widely, most leverage fundamental blockchain and cryptography concepts.
Are Cryptocurrencies Legal?
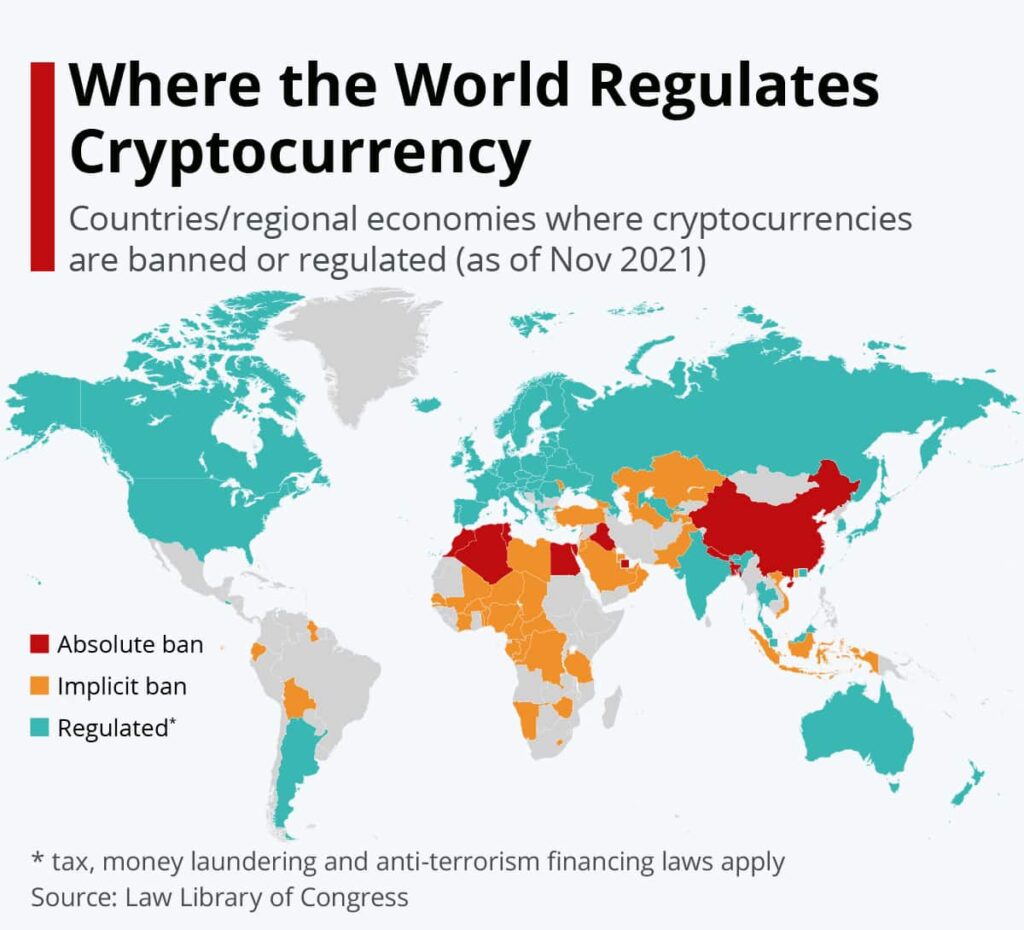
The legality of cryptocurrencies varies widely by jurisdiction. Here is an overview of how they are treated in some major economies:
In the U.S.
Cryptocurrency is legal in the United States. Entities like the Treasury Department, SEC, and CFTC provide high-level regulatory oversight and guidance. Cryptocurrencies are considered commodities or assets from a legal standpoint. Exchanges and service providers dealing with crypto are subject to registration and licensing requirements to operate legally. In general, the U.S. has taken a moderate regulatory approach focused on enforcing anti-fraud and anti-manipulation measures in the crypto space.
In Asia
- China – Cryptocurrency is effectively banned in China. Initial coin offerings (ICOs) and domestic crypto exchanges are prohibited. However, holding or mining crypto itself is not illegal.
- Japan – Japan was an early pioneer in crypto regulation, recognizing Bitcoin as legal tender in 2017. Exchanges must register with the Financial Services Agency.
- South Korea – Crypto exchanges are legal and South Korea is considered a major crypto trading hub globally. Specific regulations vary.
- India – Cryptocurrencies remain in legal limbo in India. A proposed bill could ban most cryptocurrencies while creating a regulatory framework for an official digital rupee.
In Europe
The European Union has passed landmark regulations (MiCA) to standardize crypto rules across the region focusing on licensing frameworks and supervision. Specific regulations still vary widely across individual European nations. Some like Switzerland have embraced crypto while others have restrictions.
Cryptocurrency fraud and cryptocurrency scams

Due to the irreversible and pseudonymous nature of cryptocurrency transactions, they are prone to scams and fraud. Here are some examples:
- Pump and dump schemes – Where groups artificially inflate a cryptocurrency’s price before dumping it for profit.
- Fake ICOs – Fraudsters set up fake initial coin offerings, take investors’ money, and disappear.
- Fake exchanges – Illicit exchanges fabricate trading volume or steal users deposits.
- Phishing – Scammers try to steal private keys through email phishing attacks.
- Fake wallet apps – Malicious wallet apps are published to app stores to steal crypto funds.
- Rug pulls – Developers abandon a cryptocurrency project and steal invested funds.
- Malware and ransomware – Malware that demands payment in cryptocurrency after infecting computers.
- Identity theft – Criminals may steal crypto investors’ identity information and drain their accounts.
To avoid cryptocurrency scams, only use reputable, mainstream exchanges and custody solutions and never share private keys. Be wary of unbelievable returns promised by certain tokens or platforms. As with any investing, if it seems too good to be true, it probably is.
is cryptocurrency a good investment?

Whether cryptocurrency is a good investment depends on an individual investor’s goals and risk tolerance. Here are some considerations:
Potential upside – As a emerging technology, cryptocurrencies have room for major value appreciation if adoption continues rising. The market cap of crypto still pales compared to stocks, bonds, or gold.
High volatility – Cryptocurrency prices can experience wild swings. Volatility allows for profits but also significant losses. Bitcoin lost 80% of value in 2018 before recovering.
Uncertain regulation – Evolving government oversight adds regulatory risk. China banning crypto exchanges in 2017 caused large price declines.
Cybersecurity risks – Hacking incidents and theft can wipe out funds. Exchanges have collapsed with customers losing assets.
Long term viability – Bitcoin and major cryptos have endured over a decade but risks like scalability challenges or security flaws could emerge.
Overall, cryptocurrencies represent a high-risk, high-reward investment. They hold unique advantages like decentralized finance and smart contract capabilities but also large risks like volatile prices, evolving regulation, and cybersecurity threats. Investors should carefully assess their own tolerance for risk and invest prudently.
How to store cryptocurrency

Cryptocurrency should be stored securely in digital wallets, either hosted online or offline:
- Online wallets/exchanges – Most exchanges like Coinbase provide hosted hot wallets to easily store crypto online for trading and spending. Convenient but less secure.
- Desktop wallets – Wallets downloaded locally on a PC or laptop. Provides more security than online options but less convenience. Examples: Exodus, Electrum.
- Mobile wallets – Wallets designed for smartphones. Can be used on-the-go for transactions. Examples include Trust Wallet, Coinomi.
- Hardware wallets – Physical USB devices that store private keys offline for optimal security. Costlier but ideal for large holdings. Popular options: Ledger, Trezor.
- Paper wallets – Keys printed or written on paper. Very low-tech but highly secure long-term storage option.
The most secure cryptocurrency storage involves using well-encrypted hardware or paper wallets held offline in cold storage. Online and mobile wallets provide much greater convenience but increased risk. Investors must balance security needs with usability based on their holdings and activity.
What can you buy with cryptocurrency?

While not as widely accepted as traditional currency, cryptocurrencies can be used to purchase a growing variety of goods and services:
- Buy products online – Some major retailers like Microsoft, AT&T, and Overstock.com allow purchases with Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies.
- Travel and hospitality – Travel sites CheapAir.com and Travala.com accept crypto for flights and hotels.
- Food/delivery services – DoorDash, Just Eat, and Pizza Hut in Venezuela allow crypto payments for food orders.
- Digital media – Reddit allows you to buy premium memberships with crypto. Many indie games and apps accept crypto donations.
- Gift cards – Bitrefill allows converting Bitcoin into gift cards for many other brands.
- Consumer tech – Cryptocurrency can be used to shop directly on sites like Newegg and on eBay.
- Luxury items – Some high-end retailers sell big ticket items like cars or watches to crypto holders.
- Real estate – A small but growing number of real estate companies accept cryptocurrency for property purchases.
So while day-to-day spending is still limited, crypto adoption is increasing, especially online and for larger purchases. More integration could occur if volatility decreases and regulatory clarity improves worldwide.
Read more: What Can You Buy with Bitcoin? 10 Ways to Spend Crypto in 2024
Advantages of Cryptocurrency
Here are some of the main benefits that cryptocurrencies offer compared to traditional fiat currencies:
- Decentralized – Cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks not controlled by any single entity or middleman. This helps prevent manipulation and gives users more control.
- Transparent – Transactions are recorded on public blockchains that can be independently audited and traced for transparency.
- Censorship resistant – Cryptocurrency networks are immutable and cannot be easily shut down, providing robust censorship resistance.
- Accessibility – Cryptocurrencies facilitate open access to financial services globally, especially for underbanked populations.
- Efficient – Cryptocurrency transactions are typically faster and cheaper than legacy systems due to automation and minimal overhead.
- Programmable – The programmable nature of cryptocurrencies allows developers to build a wide range of functionality and financial applications on top of them.
- Pseudonymous – User identities are generally unknown, providing increased privacy over traditional systems. However, transactions themselves are publicly visible.
- Secure – Strong cryptography underpins cryptocurrencies, making counterfeiting, hacking attacks, and fraud very difficult.
Disadvantages of Cryptocurrency
Some potential downsides and risks include:
- Volatility – With no backing and limited adoption so far, cryptocurrency prices can be highly volatile compared to assets like stocks or gold.
- Lack of regulation – Currently limited government oversight and protection for crypto investors compared to traditional securities or accounts.
- Fraud risk – Cryptocurrency systems can still be targeted for fraud, hacking, and scams due to their relative novelty and anonymity.
- Complex technology – Blockchains, digital wallets, and other aspects of crypto can be complex for mainstream individuals. Steep learning curve.
- Adoption challenges – Daily merchant/business adoption of cryptocurrencies as payment methods, while growing, remains fairly limited.
- Energy usage – Some cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin rely on proof-of-work mining which consumes substantial amounts of energy.
- Money laundering – Pseudonymity makes cryptocurrencies potentially appealing for nefarious uses like money laundering, black market transactions, tax evasion, etc.
Conclusion – What is Cryptocurrency
In conclusion, cryptocurrencies represent a major advancement in digital assets and financial technology made possible by innovations like blockchain and cryptography. They offer a decentralized, secure, transparent, and programmable alternative to traditional fiat money along with greater privacy and accessibility. However, mainstream adoption is still limited by factors like price swings, lack of regulation, complexity, and illegal usage. As the technology matures and oversight evolves, cryptocurrencies could potentially transform financial services and provide benefits over legacy systems in efficiency, accessibility, resilience, and user control. But a variety of risks and challenges must still be addressed on the path to wider acceptance.
Some other definition
What is cryptocurrency simple definition
Cryptocurrency is a form of digital currency that uses cryptography to secure transactions and control the creation of new units. Cryptocurrencies operate independently of governments or central banks. Instead, they use a decentralized system to record transactions and issue new units.
Some key features of cryptocurrency include:
- Encrypted transactions: Cryptocurrencies use cryptography and encryption to verify transfers and secure accounts. This protects the privacy of users.
- Decentralized: There is no central authority that controls cryptocurrency. Instead, it is managed by peer-to-peer networks. This avoids government manipulation or interference.
- Limited supply: Many cryptocurrencies have a limited number of units or tokens that will ever be produced. This scarcity creates value and can drive prices higher.
- Anonymity: Cryptocurrency users are identified by wallet addresses, not names. This provides a level of anonymity, although transactions can still often be traced.
In simple terms, cryptocurrency utilizes advanced math and computer science to create a secure, decentralized currency outside the control of governments and institutions. The “crypto” refers to the cryptography used to protect user identities and verify transactions.
What is cryptocurrency basic
Cryptocurrency at its most basic level is digital money that is secured by cryptography. Cryptography is used to generate units of the currency and verify transfers between users. Here are some key aspects of cryptocurrency:
- Digital: Cryptocurrency exists only in digital form, not physical coins or bills. This allows it to be transferred quickly and securely over the internet.
- Decentralized: No single entity controls the currency or transactions. A global network of computers manages everything through cryptography.
- Encrypted: Advanced cryptographic techniques are used to generate units, secure accounts, and verify transfers. This encryption protects the privacy and security of users.
- Limited supply: Many cryptocurrencies limit the total number of units that will be issued. This scarcity helps drive value and can cause prices to rise over time.
- Pseudonymous: Users are identified by wallet addresses and pseudonyms rather than personal details. This provides increased anonymity but transactions can still often be traced.
So in basic terms, cryptocurrency utilizes cryptography, a form of advanced encryption, to create digital money that is decentralized, protected, and scarce outside the control of governments and institutions. The “crypto” refers specifically to the cryptographic techniques used to secure the system.
What is cryptocurrency easy explanation
Here is an easy explanation of what cryptocurrency is:
Cryptocurrency is digital money that only exists online. It uses encryption techniques to control how units of currency are created and to verify transactions. This makes it secure and private.
Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency, started in 2009. Now there are thousands of different cryptocurrencies. Some well-known ones include Ethereum, Litecoin, and Dogecoin.
Cryptocurrencies don’t have physical coins or bills. All the units exist just as data. This makes cryptocurrency transactions fast, global, and inexpensive.
No single organization controls cryptocurrency. A network of computers around the world manage each cryptocurrency using cryptography. This decentralized system avoids central control or manipulation.
Users have unique codes called keys which allow them to prove they own cryptocurrency units. Transactions between users are recorded in a digital ledger called the blockchain which is public. User identities are secure and anonymous but transactions are transparent.
So in summary, cryptocurrencies are digital currencies secured by encryption techniques that allow fast, anonymous, global transactions outside the control of a central authority. It exists purely online but has real world value.
What is the basis of cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency is built on a foundation of several key technical and economic concepts:
Blockchain technology – The digital ledger that records all cryptocurrency transactions in a secure and transparent manner. It operates in a decentralized way across many computers.
Cryptography – Advanced encryption techniques used to secure the blockchain, protect user identities, and verify all transfers or transactions.
Decentralized control – No central bank or government controls cryptocurrency. It is managed by peer-to-peer networks and supply is controlled programmatically.
Digital scarcity – Many cryptocurrencies have a limited total supply that creates digital scarcity and provides an inherent economic value.
Mining – The process where people use computing power to maintain blockchain networks and are rewarded with cryptocurrency for their efforts.
Peer-to-peer exchange – Users can directly exchange cryptocurrency between wallets without needing an intermediary like a bank.
So in summary, cryptocurrencies leverage computer science and cryptographic techniques to create systems of programmable, decentralized money outside the control of governments, banks, and institutions. The basis is digital, mathematical, and social in nature.

