“What is a Bitcoin Wallet?” As Bitcoin’s popularity continues to soar, understanding the significance of Bitcoin wallets becomes crucial for storing, sending, and receiving digital currency. This concise guide navigates through the types of Bitcoin wallets, offering a step-by-step setup process.
Addressing common confusion, the aim is to provide clarity, empowering readers to manage digital assets effectively. Beyond technicalities, the article equips readers with practical knowledge, ensuring proficiency in various wallet types and the setup process.
With insightful details, it engages readers, offering information to clarify uncertainties and foster a comprehensive understanding of Bitcoin wallets. Essentially, it serves as a guide for individuals aiming to navigate the world of digital currency management.”
What is a Bitcoin wallet?
Exploring the practical aspect, a Bitcoin wallet, in essence, serves as a device or program facilitating the sending and receiving of bitcoins. The term “wallet” might initially perplex those new to Bitcoin and cryptocurrency. Unlike a physical wallet storing tangible currency, a Bitcoin wallet doesn’t hold bitcoins within it. This might raise the question: How does this work?
Consider the familiar item in your physical wallet right now: a debit card. Not constituting actual money, the debit card provides access to your funds. A Bitcoin wallet operates on a similar principle, but with a key distinction. While a debit card is controlled by a centralized entity, typically a bank, Bitcoin operates without central control from any individual or organization. This distinction underscores that Bitcoin wallets function differently from traditional bank accounts, necessitating unique mechanisms for secure operations.
How Bitcoin wallets work

Exploring the functionality of Bitcoin wallets involves drawing parallels with the analogy of a debit card. A Bitcoin wallet, akin to a debit card, houses at least one “account” or sub-wallet, each equipped with vital information. In the context of Bitcoin wallets, these details encompass the public bitcoin address and the private key, which play roles equivalent to a debit card’s account number and password, respectively. The private key, being a 256-bit secret number, is integral to granting access to the bitcoins associated with the public bitcoin address.
Here is an example:
108165236279178312660610114131826512483935470542850824183737259708197206310322
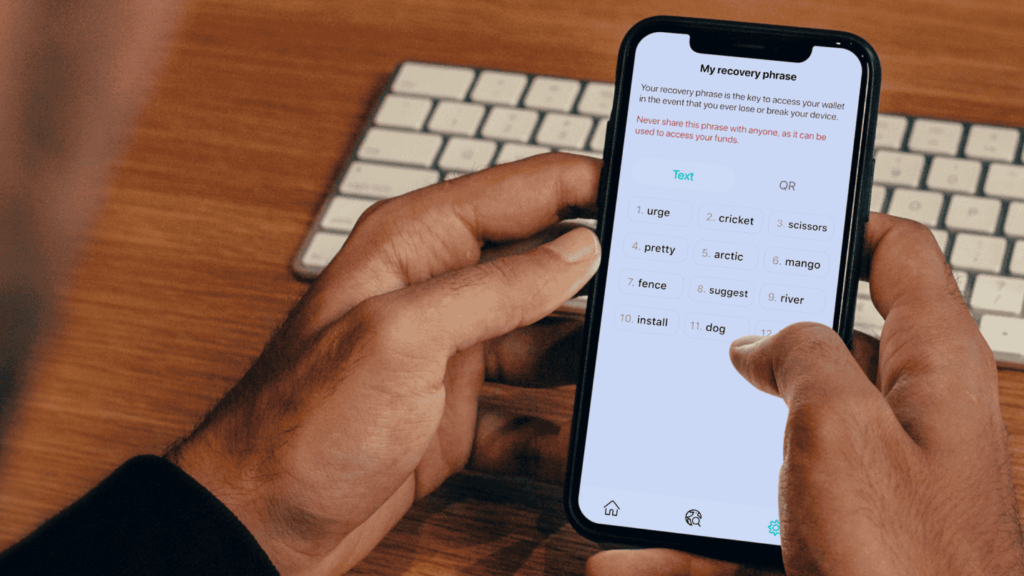
The management of the private key is a crucial aspect handled by Bitcoin wallets, sparing users from direct interaction with these complex cryptographic elements. Instead, Bitcoin wallets offer a user-friendly alternative by allowing the private key to be recorded in a more human-readable format, referred to as a recovery phrase, secret passphrase, or seed phrase. Typically consisting of 12 to 24 words, a recovery phrase serves as a safeguard, enabling users to reconstruct their Bitcoin wallet and access funds even in the event of the wallet being destroyed.
While the recovery phrase improves upon the unwieldy nature of the private key, security considerations caution against storing it in plain text on computers or online. The recommended practice is to record the recovery phrase on paper, despite the challenges associated with securely storing physical documents. However, managing multiple recovery phrases, especially in a multi-coin wallet supporting various blockchains like the Bitcoin.com Wallet, can become cumbersome.
Addressing this challenge, the Bitcoin.com Wallet incorporates a “Cloud Backup” system. This feature allows users to create a single custom password, unlocking all private keys stored in encrypted form in their Google or iCloud account. To set up Cloud Backup in the Bitcoin.com Wallet, users can navigate to Settings > Cloud Backup and follow the provided instructions. This integration enhances both the security and convenience of managing private keys, offering users a streamlined solution for safeguarding their Bitcoin assets.
Types of Bitcoin Wallets
Just like traditional wallets, Bitcoin wallets come in various styles, each presenting a balance between convenient access and security against theft.
Mobile Wallets Mobile wallets, such as the WazirX multi-cryptocurrency wallet and Exodus bitcoin wallet, function as applications on smartphones, tablets, and other mobile devices.
Web Wallets Web-based wallets, exemplified by the Guarda Bitcoin Wallet, store coins through an online third party. Accessible from any internet-connected device, these wallets are often linked to crypto exchanges, offering a consolidated platform for trading and storage. Despite their convenience, web wallets share similar risks with mobile wallets, including susceptibility to hacking.
Desktop Wallets Desktop wallets, like Guarda and Exodus, are downloadable programs installed on a computer to store coins locally. This adds an extra layer of security compared to web and mobile wallets, as you’re not reliant on third-party services. However, desktop wallets are not entirely immune to hacks due to the computer’s internet connection.
Hardware Wallets Hardware wallets, physical devices like USB drives, operate offline. Examples include the Ledger Nano X Bitcoin Wallet and Trezor Model T Bitcoin Wallet. To conduct transactions, the hardware wallet must connect to the internet, either directly or through another device. This extra step enhances security, but the process involves additional passwords, introducing the risk of locking yourself out if forgotten. Hardware-based crypto wallets are often referred to as cold storage, in contrast to internet-connected hot wallets.
Paper Wallets In a paper wallet, the key, typically a QR code, is printed on a physical document. This method eliminates the risk of online hacking but introduces the challenge of safeguarding the physical document.
Choosing a Bitcoin wallet involves assessing your priorities between accessibility and security, considering the unique features and risks associated with each type.
Bitcoin Wallet Security
The security of your crypto wallet is paramount, given the attractiveness of cryptocurrencies as targets for hackers. Implementing robust safeguards is crucial to protect your digital assets. One fundamental measure involves encrypting your wallet with a strong password, fortifying its defense against unauthorized access. For exchanges, adopting two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security, and for significant amounts, storing funds offline is a prudent strategy.
Malware disguised as wallets poses a considerable threat, making diligent research imperative before selecting a wallet. Vigilance is key, as a compromised wallet could lead to unauthorized access to your cryptocurrency holdings.
Seed Words: Modern wallets typically generate a twelve-word mnemonic seed phrase, such as “airport bedroom impression sample reception protection road shirt.” Despite appearing random, this phrase is intricately linked to your keys by your wallet. Safeguarding this seed phrase is critical, as anyone who gains access can potentially compromise your cryptocurrency holdings. These seed words serve as a recovery mechanism in case your device is lost or damaged.
Cryptocurrency Exchanges: While some cryptocurrency exchanges offer custodial key storage services, exercising caution is essential. Cryptocurrency exchanges are prime targets for cybercriminals, and entrusting them with your assets carries inherent risks. In the event of a business closure or bankruptcy, the security of your cryptocurrency held by the exchange may be at risk. For instance, Coinbase’s disclosure to the Securities and Exchange Commission highlights the potential vulnerability of custodially held crypto assets in the event of bankruptcy.
Cold Storage for Enhanced Security: Optimal cryptocurrency key security involves transferring your keys from your wallet to a form of cold storage, such as a vault, safe, or deposit box. The objective is to create additional layers of protection, making it more challenging for criminals to gain unauthorized access. The multifaceted approach not only safe guards your keys but also mitigates the risk of losing access due to the bankruptcy or malfeasance of a custodial wallet provider.
How to Choosing the Optimal Cryptocurrency Wallet
Selecting the right cryptocurrency wallet is a pivotal decision given the multitude of options available. It is advisable to peruse numerous reviews, ensuring that the chosen wallet aligns with your specific needs while prioritizing the security of your cryptographic keys.
Determining the Safest Crypto Wallet:
The paramount consideration for the safest crypto wallet is its complete detachment, both from external devices and the internet. Furthermore, it should not jeopardize your access to cryptocurrency in the event of financial issues affecting the custodian. It is crucial to be wary of wallets labeled as “safe” that may incorporate wireless connection technology, potentially exposing vulnerabilities to determined cybercriminals.
Necessity of a Cryptocurrency Wallet:
Undoubtedly, having a cryptocurrency wallet is imperative. Your private keys, essential for accessing your cryptocurrency, require a secure storage interface that interacts with a blockchain. While all wallets are equipped to store keys, it’s crucial to note that only hot wallets have the capability to directly access the blockchain. Therefore, a prudent approach involves keeping your keys off the hot wallet until they are actively needed.
Investing in cryptocurrencies and participating in Initial Coin Offerings (“ICOs”) entail considerable risk and speculation. This article does not serve as a recommendation by Investopedia or the author to invest in cryptocurrencies or ICOs. As financial decisions are highly individualized, consulting with a qualified professional is essential before making any investment choices. Investopedia disclaims any representations or warranties regarding the accuracy or timeliness of the information provided herein.
source: https://developer.bitcoin.org/

